EKG Rhythm Strip Quiz 43
Identify the following rhythms
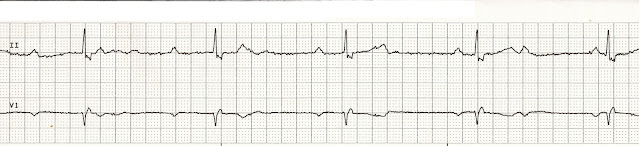
1.
a. 3rd degree heart block
c. Atrial fibrillation
d. 2nd degree heart block type II
2.
a. Atrial paced
c. AV pacing
d. Biventricular pacing
3.
a. Bradycardia with sinus arrhythmia
c. Complete heart block
d. Junctional rhythm
4.
a. Sinus bradycardia with atrial ectopic beats
c. Sinus tachycardia with frequent unifocal PVCs
d. Sinus rhythm with multifocal PVCs
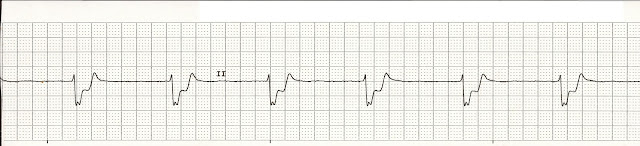
5.
a. Complete heart block
b. Junctional rhythm
c. Agonal rhythm
d. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
6.
a. Ventricular unigeminy
b. Ventricular bigeminy
c. Ventricular trigeminy
d. Ventricular quadrigeminy
7.
a. Normal sinus rhythm with T wave inversion
b. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
c. Accelerated junctional rhythm ST elevation
d. Idioventricular rhythm with ST depression
8.
a. Normal sinus rhythm with 1st degree block
b. Sinus bradycardia
c. Atrial flutter
d. 2nd degree heart block type II
9.
a. Sinus arrhythmia
c. Atrial fibrillation with controlled ventricular response
d. Wandering atrial pacemaker
10
a. Atrial flutter with variable rate
b. 2nd degree heart block type II
c. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
d. Sinus tachycardia with sinus pauses
Answers
1.
a. 3rd degree heart block. There is no relationship between the P waves and the QRS complexes.
2.
c. AV pacing. Demand atrial pacing on the 7th complex.
3.
b. Idioventricular rhythm. Wide, slow, and bizarre looking QRS complexes characterize this rhythm.
4.
b. Normal sinus rhythm with PACs. The early beats will have a P wave that is shaped differently from the sinus beats. Also notice that in some cases the P waves are buried within the preceding T wave thus changing the shape or height of the P wave.
5.
c. Agonal rhythm. Wide, slow, and bizzare QRS complexes with an underlying rate of less than 20 beats per minute. Agonal beats represent the terminal changes of an idioventricular rhythm. In other words, the patient is dying.
6.
c. Ventricular trigeminy There is a PVC every 3rd beat.
7.
a. Normal sinus rhythm with T wave inversion (in lead II) This may represent ischemic changes to the myocardium.
8.
d. 2nd degree heart block type II. There are P waves with dropped QRS complexes. The PR interval is consistent on the conducted beats. Recall, that on a Mobitz I block that the PR interval increases over consecutive beats.
9.
a. Sinus arrhythmia. The R-R interval is irregular.
10.
a. Atrial flutter with variable rate.
Reviewed 6/4/13, 3/6/16
a. 3rd degree heart block
c. Atrial fibrillation
d. 2nd degree heart block type II
2.
a. Atrial paced
c. AV pacing
d. Biventricular pacing
a. Bradycardia with sinus arrhythmia
c. Complete heart block
d. Junctional rhythm
4.
a. Sinus bradycardia with atrial ectopic beats
c. Sinus tachycardia with frequent unifocal PVCs
d. Sinus rhythm with multifocal PVCs
5.
a. Complete heart block
b. Junctional rhythm
c. Agonal rhythm
d. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
6.
a. Ventricular unigeminy
b. Ventricular bigeminy
c. Ventricular trigeminy
d. Ventricular quadrigeminy
7.
a. Normal sinus rhythm with T wave inversion
b. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
c. Accelerated junctional rhythm ST elevation
d. Idioventricular rhythm with ST depression
8.
a. Normal sinus rhythm with 1st degree block
b. Sinus bradycardia
c. Atrial flutter
d. 2nd degree heart block type II
9.
a. Sinus arrhythmia
c. Atrial fibrillation with controlled ventricular response
d. Wandering atrial pacemaker
10
a. Atrial flutter with variable rate
b. 2nd degree heart block type II
c. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
d. Sinus tachycardia with sinus pauses
Answers
1.
a. 3rd degree heart block. There is no relationship between the P waves and the QRS complexes.
2.
c. AV pacing. Demand atrial pacing on the 7th complex.
3.
b. Idioventricular rhythm. Wide, slow, and bizarre looking QRS complexes characterize this rhythm.
4.
b. Normal sinus rhythm with PACs. The early beats will have a P wave that is shaped differently from the sinus beats. Also notice that in some cases the P waves are buried within the preceding T wave thus changing the shape or height of the P wave.
5.
c. Agonal rhythm. Wide, slow, and bizzare QRS complexes with an underlying rate of less than 20 beats per minute. Agonal beats represent the terminal changes of an idioventricular rhythm. In other words, the patient is dying.
6.
c. Ventricular trigeminy There is a PVC every 3rd beat.
7.
a. Normal sinus rhythm with T wave inversion (in lead II) This may represent ischemic changes to the myocardium.
8.
d. 2nd degree heart block type II. There are P waves with dropped QRS complexes. The PR interval is consistent on the conducted beats. Recall, that on a Mobitz I block that the PR interval increases over consecutive beats.
9.
a. Sinus arrhythmia. The R-R interval is irregular.
10.
a. Atrial flutter with variable rate.
Reviewed 6/4/13, 3/6/16











Comments
Post a Comment