Basic EKG Rhythm Test 07
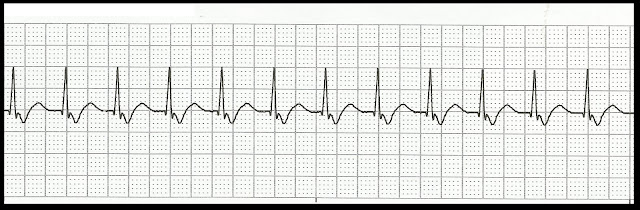
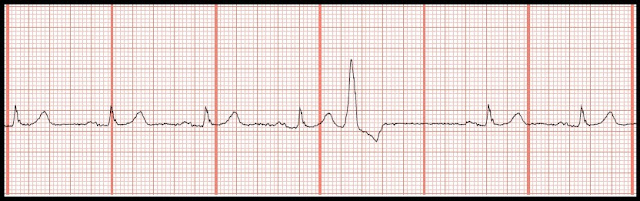
Identify the following rhythms. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Do you want to try another Basic EKG Rhythm Test? Click here. Answers 1. Junctional tachycardia 2. Accelerated junctional rhythm 3. Atrial paced 4. Normal sinus rhythm with PACs 5. Sinus rhythm changing to ventricular tachycardia 6. Supraventricular tachycardia 7. Ventricular tachycardia changing to ventricular fibrillation 8. 2nd degree heart block type I 9. Atrial fibrillation with multifocal PVCs 10. Idioventricular rhythm 11. Normal sinus rhythm with a multifocal couplet 12. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia 13.
.jpg)
