Basic EKG Rhythm Test 04
EKG Rhythm Practice Test
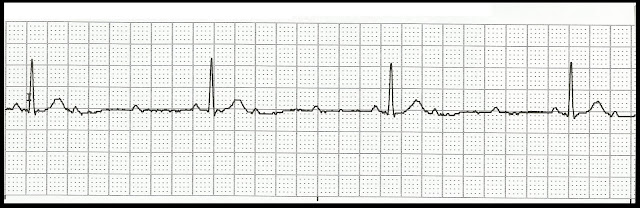
Identify the following rhythms.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15
16
17.
18.
19.
20.

21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
For another Basic EKG Rhythm Test click here
Answers
1. 2nd degree AV block type I
Notice how the PR interval is increasing over successive beats. THE KEY TO IDENTIFYING HEART BLOCKS IS TO LOOK AT THE PR INTERVAL.
2. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
Idioventricular rate 20-40, accelerated idioventricular rate 40-100
3. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
4. Atrial paced
5. Junctional rhythm
Inverted P waves precede the QRS complex
6. Normal sinus rhythm with artifact
60 cycle electrical interference
7. Sinus bradycardia
8. Torsades de pointe
9. Ventricular fibrillation
10. Ventricular tachycardia
11. Agonal rhythm
12. 2nd degree AV block type II
The PR interval on the conducted beats is the same. Also there are some nonconducted P waves
13. Complete heart block
No association between the P waves and the QRS complexes. Some P waves buried within the QRS complex. Compare this to rhythm 1 and 12.
14. Idioventricular rhythm
Slow wide rhythm is ventricular in origin. Sometimes this is an irregular rhythm
15. Normal sinus rhythm with ventricular trigeminy
16. Junctional tachycardia
Inverted P waves that follow the QRS complex
17. Atrial tachycardia
There are some small P waves present. PR interval is shortened.
18. Ventricular fibrillation
19. Ventricular paced
20. Ventricular tachycardia changing to ventricular fibrillation
21. AV paced
22. Aystole
23. Normal sinus rhythm with PJCs
Notice that the 2nd and 9th complexes are early and have an inverted P wave
24. Normal sinus rhythm with couplets of PVCs
25. Sinus arrhythmia
The R-R interval varies. There is no change in the morphology of the P waves to suggest that there are premature atrial complexes present.
Identify the following rhythms.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15
16
17.
18.
19.
20.

21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
For another Basic EKG Rhythm Test click here
Answers
1. 2nd degree AV block type I
Notice how the PR interval is increasing over successive beats. THE KEY TO IDENTIFYING HEART BLOCKS IS TO LOOK AT THE PR INTERVAL.
2. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
Idioventricular rate 20-40, accelerated idioventricular rate 40-100
3. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response
4. Atrial paced
5. Junctional rhythm
Inverted P waves precede the QRS complex
6. Normal sinus rhythm with artifact
60 cycle electrical interference
7. Sinus bradycardia
8. Torsades de pointe
9. Ventricular fibrillation
10. Ventricular tachycardia
11. Agonal rhythm
12. 2nd degree AV block type II
The PR interval on the conducted beats is the same. Also there are some nonconducted P waves
13. Complete heart block
No association between the P waves and the QRS complexes. Some P waves buried within the QRS complex. Compare this to rhythm 1 and 12.
14. Idioventricular rhythm
Slow wide rhythm is ventricular in origin. Sometimes this is an irregular rhythm
15. Normal sinus rhythm with ventricular trigeminy
16. Junctional tachycardia
Inverted P waves that follow the QRS complex
17. Atrial tachycardia
There are some small P waves present. PR interval is shortened.
18. Ventricular fibrillation
19. Ventricular paced
20. Ventricular tachycardia changing to ventricular fibrillation
21. AV paced
22. Aystole
23. Normal sinus rhythm with PJCs
Notice that the 2nd and 9th complexes are early and have an inverted P wave
24. Normal sinus rhythm with couplets of PVCs
25. Sinus arrhythmia
The R-R interval varies. There is no change in the morphology of the P waves to suggest that there are premature atrial complexes present.
















+03.jpg)









Comments
Post a Comment