Practice EKG Rhythm Strips 158
Identify the following rhythms
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Answers
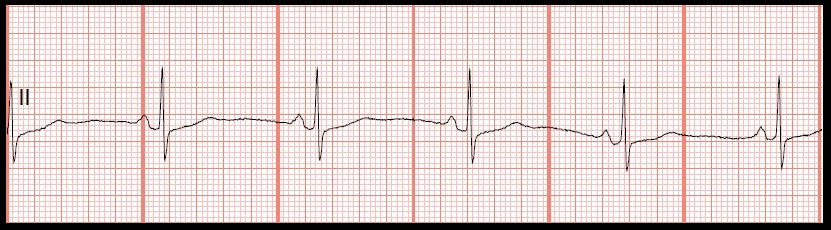
1.
The rhythm is regular and the rate is 53/min. There are upright P waves before each QRS complex. No ectopic beats are present. PR: .16 sec, QRS: .08 sec, QT: .44 sec.
2.
The rhythm is irregular because of the unifocal PVCs. The rate is 110. With the exception of the PVCs, the P waves are upright, uniform, and precede the QRS complexes. There are unifocal trigeminal PVCs present. The PVCs may be fusion complexes as there appears to be a P wave present right before the initial upstroke of the R wave. The P-P distance tends to substantiate this. PR: .20 sec, QRS: 08 sec, QT: .36 sec.
3.
The rhythm is regular with a rate of 62. No P waves are readily identified. No ectopy is noted. PR: ---, QRS: .06 sec, QT: .36 sec. Based upon the rate, the rhythm is identified as an accelerated junctional rhythm which has a rate between 60 and 100.
4.
The rhythm is very irregular. The rate is 170/min. No readily identifiable P waves are present. No ectopy is noted. The rhythm could be classified as a supraventricular tachycardia but because of the very irregular rhythm it is more than likely and atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. Another possibility could be a multifocal atrial tachycardia. PR: ---, QRS: .10 sec. QT: .28 sec. If the patient is unstable then cardioversion would be an option. One could attempt to control the rate with a beta blocker, calcium channel blocker, or antiarrhythmic. Attention would be given to ruling out an atrial thrombus prior to cardioversion.
5.
This is an example of 60 cycle electrical interference.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Answers
1.
 |
| Sinus bradycardia |
The rhythm is regular and the rate is 53/min. There are upright P waves before each QRS complex. No ectopic beats are present. PR: .16 sec, QRS: .08 sec, QT: .44 sec.
2.
 |
| Sinus tachycardia with trigeminal PVCs |
The rhythm is irregular because of the unifocal PVCs. The rate is 110. With the exception of the PVCs, the P waves are upright, uniform, and precede the QRS complexes. There are unifocal trigeminal PVCs present. The PVCs may be fusion complexes as there appears to be a P wave present right before the initial upstroke of the R wave. The P-P distance tends to substantiate this. PR: .20 sec, QRS: 08 sec, QT: .36 sec.
3.
 |
| Accelerated junctional rhythm |
The rhythm is regular with a rate of 62. No P waves are readily identified. No ectopy is noted. PR: ---, QRS: .06 sec, QT: .36 sec. Based upon the rate, the rhythm is identified as an accelerated junctional rhythm which has a rate between 60 and 100.
4.
 |
| Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response |
The rhythm is very irregular. The rate is 170/min. No readily identifiable P waves are present. No ectopy is noted. The rhythm could be classified as a supraventricular tachycardia but because of the very irregular rhythm it is more than likely and atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. Another possibility could be a multifocal atrial tachycardia. PR: ---, QRS: .10 sec. QT: .28 sec. If the patient is unstable then cardioversion would be an option. One could attempt to control the rate with a beta blocker, calcium channel blocker, or antiarrhythmic. Attention would be given to ruling out an atrial thrombus prior to cardioversion.
5.
 |
| Artifact 60 cycle interference |
This is an example of 60 cycle electrical interference.







Comments
Post a Comment