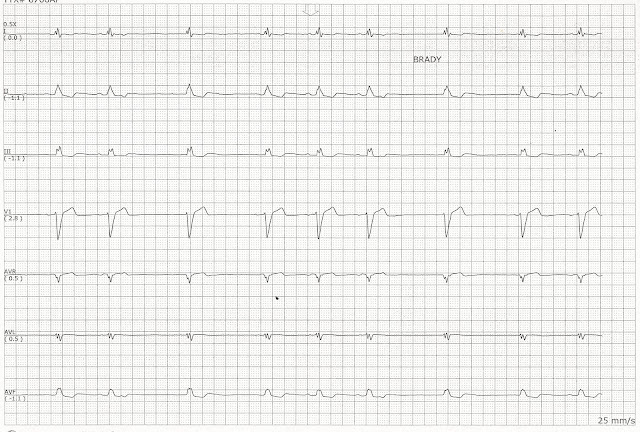
Identify the following rhythms. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Answers 1. Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response The rhythm is irregular with a ventricular rate of 50/min. No P waves are seen but there is fibrillatory activity between the QRS complexes. No ectopic beats are seen. PR: ---, QRS: .08 sec, QT: .42 sec. 2. NSR with ventricular bigeminy The rhythm is irregular with a rate of 70/min. The P waves are upright, uniform, and paired with a QRS complex. There are PVCs every other beat. PR: .20 sec, QRS: .12 sec, QT: .44 sec 3. Atrial fibrillation with ventricular demand pacing and a PVC The rhythm is irregular. The rate is 70/min. No P waves are present. There is a single PVC present, the 5th complex. The 1st and 6th complexes are ventricular paced beats while the remaining complexes are the patient...